What is a pressure vessel? Explain the difference between Type 1 and Type 2 pressure vessels

Pressure vessels play an important role in many industries, and their correct understanding and safe use are required. Pressure vessels are mainly used to hold liquids and gases at high pressure, and are widely used in Chemical Industrial, Oil, and Food industries. In order to ensure safety and applicability, in-depth knowledge of design standards and usage is required.
In this column, we will explain the type of pressure vessel and explain our proposed products.
 Example of appearance of pressure vessel
Example of appearance of pressure vessel
- Types, characteristics, and applications of pressure vessels
- Difference between Type 1 Pressure Vessel and Type 2 Pressure Vessel
- Classification of Type 1 Pressure Vessel
- Application category of Type 2 pressure vessel
- Pressure vessel design standards and safety regulations
- Points for choosing a pressure vessel
- Liquid tank (pressure vessel) of Musashi Engineering
Types, characteristics, and applications of pressure vessels
Pressure vessels are broadly divided into Type 1 pressure vessels and Type 2 pressure vessels. By understanding the characteristics, it is possible to select the optimum pressure vessel according to the appropriate application.
Difference between Type 1 Pressure Vessel and Type 2 Pressure Vessel
The Type 1 Pressure Vessel and Type 2 Pressure Vessel have different design standards and regulations, so appropriate selection is required according to the application and the pressure being handled. Since first-class pressure vessels often handle high-pressure gases, strict safety standards are required by design. For example, reactors and boilers in chemical factories are designed as Type 1 pressure vessels to withstand high temperatures and high pressures and to prevent leakage of content.
On the other hand, type 2 pressure vessels often handle lower pressure compared to type 1, so safety standards are also acceptable. Type 2 pressure vessels are applied to applications that are relatively safe, such as household gas cylinders and compressed air tanks for small and medium-sized enterprises. As a result, cost and ease of installation are often prioritized.
In this way, when choosing a pressure vessel, it is important to carefully consider its application and the required pressure conditions. By selecting an appropriate type of pressure vessel, it is possible to achieve efficient operation while ensuring safety. Understanding the difference between Type 1 pressure vessels that handle high pressure and Type 2 pressure vessels that can ensure safety at low pressure is essential for the selection and operation of appropriate equipment.
Classification of Type 1 Pressure Vessel
The Type I pressure vessel is a large pressure vessel of a scale that does not fall under any of the (simple) containers and small pressure vessels specified in Article 1, Item 5 of the Enforcement Order of the Occupational Safety and Health Act. Inspection by the prefectural labor bureau at each stage of import, installation, etc. is required. After the start of use, a performance inspection by a registered performance inspection organization is required once a year.
Article 1, Item 5 of the Order for Enforcement of the Occupational Safety and Health Act
The following containers (containers used with a gauge pressure of 0.1 MPa or less, with an internal volume of 0.04m3 or less, or with an internal diameter of 200mm or less, and a length of 1000mm or less, and the maximum gauge pressure used is 0.004 or less, excluding containers with an internal volume of 0.004 or less.)
A container that accepts steam Other heat medium or generates steam to heat solids or liquids, and whose pressure in the container exceeds atmospheric pressure (excluding containers listed in b or c)
(B) A container that generates steam due to chemical reactions in containers and nuclear reactions in Other, whose pressure in containers exceeds atmospheric pressure
(C) A container that heats the liquid and generates steam in order to separate the components of the liquid in the container, and whose pressure in the container exceeds atmospheric pressure.
In addition to the containers listed from Nii to C, containers that hold liquids at temperatures above the boiling point at atmospheric pressure are inside
The application category is as follows.
(1) Classification based on maximum operating pressure and internal volume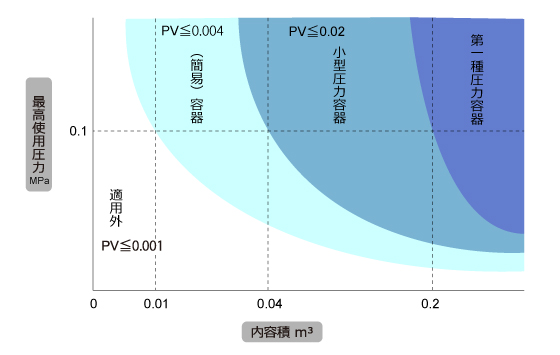
(2) Classification by internal diameter and length of the body (maximum use pressure ≤ 0.1MPa)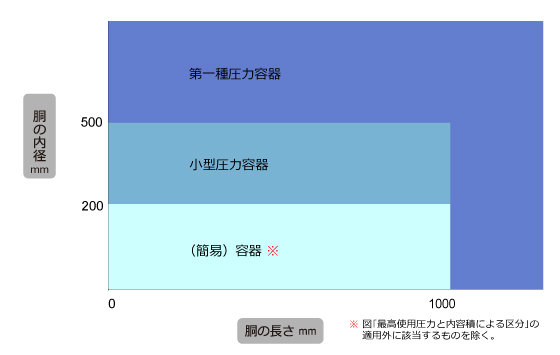
Application category of Type 2 pressure vessel
Type 2 pressure vessel is a pressure vessel specified in Article 1, Item 7 of the Order for Enforcement of the Occupational Safety and Health Act, and is larger than a (simple) container. It is mandatory to take individual tests at the time of manufacture, manufacture, or import based on the Type 2 pressure vessel structural standards, and conduct periodic voluntary inspections once a year.
Article 1, Item 7 of the Order for Enforcement of the Occupational Safety and Health Act
Type 2 pressure vessel gauge pressure of 0.2 MPa or more (excluding Type 1 pressure vessels) inside the vessel, the following containers are:
B Containers with an internal volume of 0.04m3 or more
(B) Containers with an inner diameter of 200 mm or more and a length of 1000 mm or more
The application category is as follows.
(1) Classification based on maximum operating pressure and internal volume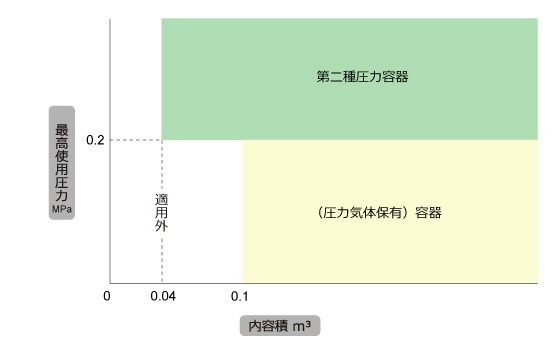
(2) Classification based on the inner diameter and length of the body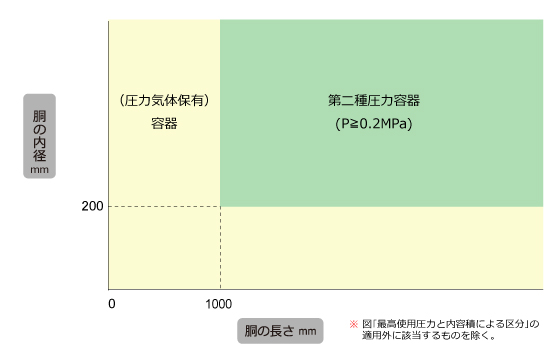
Please refer to the link below for detailed information on the application categories of various pressure vessels.
・Classification of Type 1 Pressure Vessel (Small Pressure Vessel) (https://www.jbanet.or.jp/examination/classification/vessel-1/)
・Type 2 Pressure Vessel (Japan Boilers Association) (https://www.jbanet.or.jp/examination/classification/vessel-2/)
Pressure vessel design standards and safety regulations
The design standards and safety regulations of pressure vessels are very important to ensure product safety and user reliability. By complying with appropriate standards and regulations, it is possible to reduce risks and prevent accidents.
Domestic and international regulatory standards and safety standards
In the installation and operation of pressure vessels, it is necessary to comply with domestic and international regulatory standards and safety standards. These regulatory and safety standards are established to prevent accidents and ensure the safety of users. By following this, the risk can be minimized.
For example, in Japan, inspection and certification of pressure vessels are required under the High Pressure Gas Safety Act. This law confirms that safety standards are met at each stage of manufacturing, installation, and use, and thoroughly implements measures to prevent accidents in the unlikely event of an accident. On the other hand, the "ASME Boiler and Pressure Vessel Code" is widely recognized internationally and is observed in many countries. This code is developed by the American Association of Mechanical Engineers (ASME) and provides detailed regulations ranging from design, material selection, manufacturing and testing.
Points for choosing a pressure vessel
- Use pressure
- Internal volume of containers
- Temperature conditions
- Purpose of Use and Environment
When selecting a pressure vessel, it is important to select the appropriate size and material according to its purpose. Using a pressure vessel that does not fit the purpose reduces safety and efficiency and increases the risk of accidents. Therefore, by selecting the material suitable for the application, it is possible to operate reliably over the long term.
For example, chemical factories often deal with corrosive substances, so it is recommended to choose a stainless steel pressure vessel with high corrosion resistance. On the other hand, for air compressors, a lightweight and durable aluminum pressure vessel is suitable. By choosing the right size and material, it ensures safety and efficiency and enables long-term operation.
It is important to maintain and manage pressure vessels on a regular basis to detect problems early. Regular inspection and maintenance work can detect deterioration and damage of the pressure vessel at an early stage and prevent accidents. In addition, operating costs can be reduced by preventing sudden failures.
Liquid tank (pressure vessel) of Musashi Engineering
Musashi Engineering's liquid tank is a liquid tank that realizes continuous operation of large flow applications.
We offer 4 types of safety lock tanks, straight one touch tanks, one touch tanks, and gallon tanks to accommodate a wide range of viscosity, properties and applications of liquid materials. There are two types of liquid materials: direct input type and inner container type, with a wide variety of sizes ranging from 0.5L to 38.5L, please select the most suitable tank according to your daily usage. Can also be used for liquid Filling for syringes.
※We do not manufacture first-class pressure vessels.
Essential components of liquid tank

Point of tank configuration selection
※The following 124710 corresponds to the number of "Required components of liquid tank" in the figure above.
①Tank sizeThe size is indicated in the effective volume of the tank. When using material cans or inner containers, be sure to check if the size is fit.
②O-ring for lidFor the O-ring, select a material that is difficult to expand according to the material to be inserted.
④Suction pipe⑦Liquid feed tube
The suction pipe and the liquid transmission tube are in diameter and length, respectively, and the flow rate varies greatly.
⑩Piston for inner containers (for 1kg cans)
It is essential for pressure transmission of high viscosity materials. In the case of grease or viscous adhesive, the material is consumed in a mortar shape without piston, and it is not possible to pump well.
In the case of grease or viscous adhesive, the material is consumed in a mortar shape without piston, and it is not possible to pump well.
The standard specification is a general 1kg can.
Inner diameter: It matches the size of Φ108.
It is also possible to manufacture custom-made products according to the container used by the customer.
※We will borrow a container (even used) for measurement.
Options to support simple and secure work
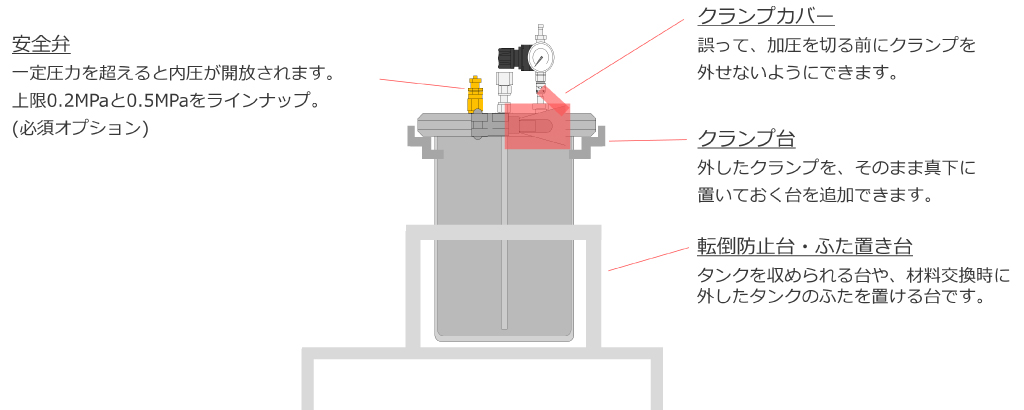
Musashi Engineering is able to propose solutions for these pressure vessels and application systems that incorporate pressure vessels in line with customer requests.
Please feel free to contact us from here.
Liquid Tank Product Lineup
・Clamp type that is easy to open and close
・Straight structure that makes it easy to put containers as they are
・Multiple hand knob clamps securely lock
・With fall prevention and fixing flange
・Inner buff polishing which can directly insert materials
・Significant reduction of material loss by combined with the downside specification
・A simple tank dedicated to direct input of liquid materials.
・Ideal for low pressure transmission of low and medium viscosity liquid materials.
・Safety structure that cannot open the lid during pressurization.
・Ideal for subdividing from liquid container to syringe
・Easy bubbleless Filling
Recommended catalog
Part Accessories & Valves/Tank Catalog

Valve tank

※Login registration is required.












